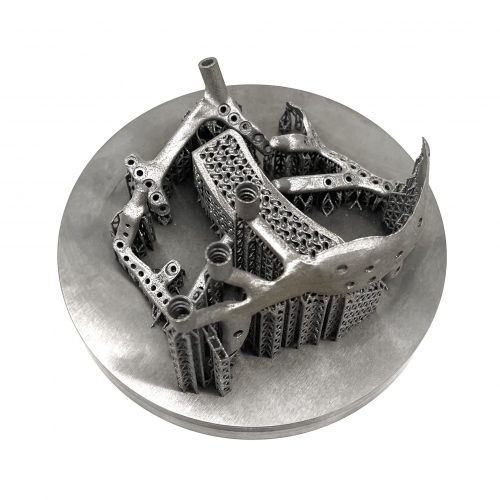
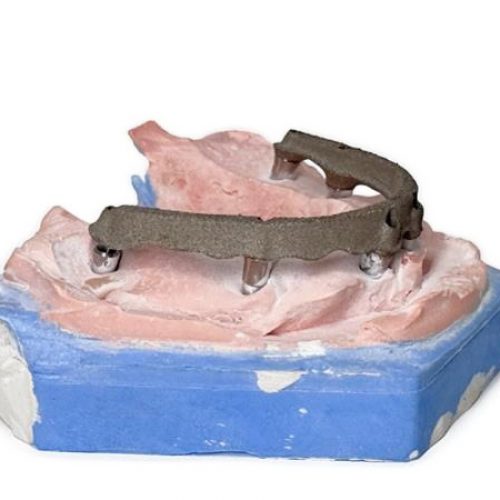
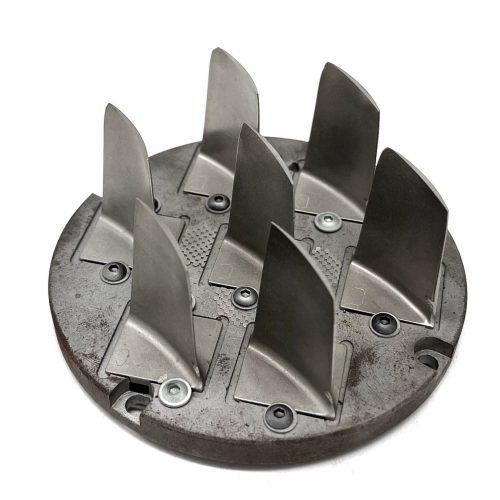
Titanium 3D printing differs from CoCr or stainless steel printing in material handling, process parameters, and technical requirements. Modern titanium 3D printers based on Powder Bed Fusion enable high-precision, biocompatible components, making the material ideal for medical and dental applications.
This guide covers key properties, powders, processes, and best practices.
Key Points in Brief:
- High Performance Material: Titanium is lightweight, strong, corrosion resistant.
- Titanium 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing via precise layer by layer Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF/EBPBF).
- Wide Range of Uses: medical, dental, aerospace, motorsport, industrial.
- Tailored Powders: optimized for specific applications and properties.
Material Properties of Titanium
Titanium and its alloys offer outstanding characteristics:
- High corrosion resistance – thanks to a protective oxide layer
- Excellent strength-to-weight ratio – lighter than stainless steel with comparable stability
- Biocompatibility – ideal for medical applications such as implants or dental prosthetics
Applications of Titanium 3D Printing
Thanks to its versatile properties, titanium 3D printing is used across multiple industries:
- Medical Technology: Ideal for implants and prosthetics due to high biocompatibility and strength
- Dental Sector: Well-suited for dental restorations and customized implantology solutions
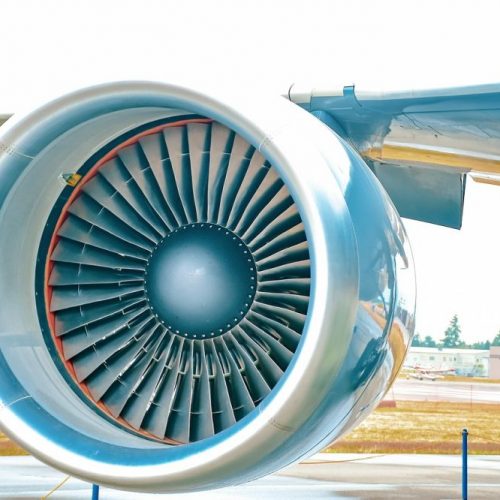
- Aerospace: Used for highly stressed and corrosion-resistant components
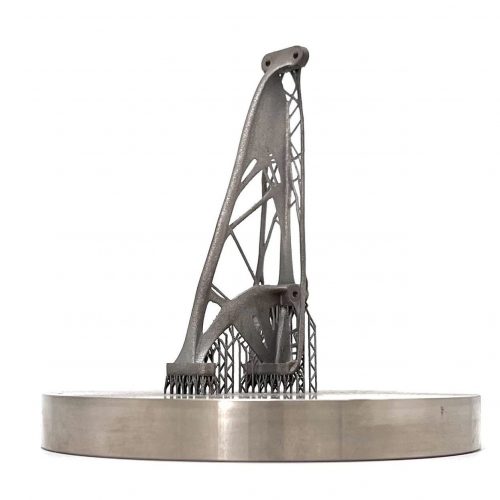
- Industry & Toolmaking: For complex geometries, e.g., components with integrated cooling
- Automotive Engineering: Especially in motorsports – for exhaust systems and suspension parts
Titanium 3D Printers and Printing Processes
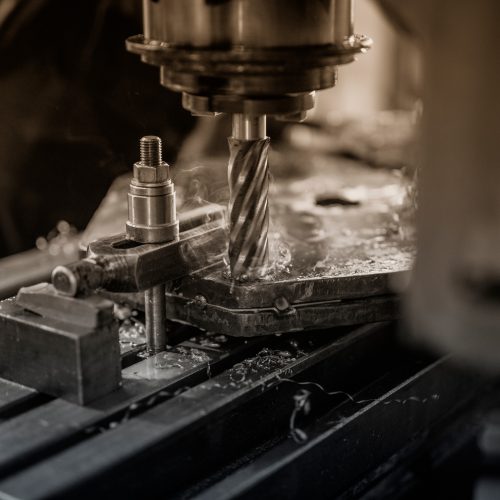
Titanium is mainly 3D printed using Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) with a laser (LPBF) or electron beam (EBPBF). In LPBF, an inert gas like argon protects the powder, while EBPBF operates in a vacuum.
Thin layers of titanium powder are spread and melted layer by layer. Support structures prevent warping, and after printing, parts are cooled and undergo post-processing such as stress-relief annealing and surface finishing to ensure dimensional accuracy and optimal material properties.
This process produces high-precision, complex titanium components for medical, dental, aerospace, motorsport, and industrial applications.
Titanium Powders for 3D Printing
Titanium 3D printing uses several specialized powders for different applications:
- Ti6Al4V (Grade 5 or 23) – most common, ideal for medical implants, dental restorations, and industrial parts.
- Beta 21S – for high-strength applications like aerospace and motorsport.
- Grade 4 (pure titanium) – corrosion-resistant , suitable for chemical, marine, and biomedical parts.
- TA15 – optimized for aerospace and specialized high-performance applications.
Switching from CoCr to Titanium
Steps for changing from CoCr to Titanium:
1. Remove powder – Fully clean the machine of CoCr residue
2. Replace filters – Change exhaust, pre-, and main filters
3. Change process gas – Use argon instead of nitrogen
4. Change build platform – Only print titanium on a titanium platform
5. Load titanium powder– Fill according to system specifications
6. Set parameters – Apply titanium-specific settings via 2Connect
Conclusion – Titanium 3D Printing
Titanium 3D printing requires a clean, controlled, and precise approach—from powder handling and gas selection to the right build platform.
With proper equipment, optimized parameters, and protective gear, the full potential of titanium can be realized, particularly in medical and dental applications, where biocompatibility, precision, and reliability are essential.

Discover the Full Potential of Titanium 3D Printers with 2onelab
Choose 2onelab – with the 2Create and 2Create Plus titanium 3D printers for dental, medical, industrial, and R&D use.
Boost quality, cut costs, and work faster – powered by cutting-edge tech and real-world expertise.
Contact us for more information!
FAQ: Titanium 3D Printing
Can You 3D Print Titanium, and How?
Yes. Titanium is 3D printed using Powder Bed Fusion (PBF). In LPBF, argon protects the powder; EBPBF uses a vacuum. Powder is fused layer by layer with a laser or electron beam. Support structures prevent warping, and post-processing ensures dimensional accuracy.
What Are the Advantages of Titanium in 3D Printing?
Titanium offers high corrosion resistance, excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good biocompatibility, and low thermal expansion.
How Strong Is 3D Printed Titanium?
3D printed titanium, like Ti6Al4V, has a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent durability. With proper PBF and post-processing,it is suitable for medical, aerospace, and high-performance industrial applications.
Which Titanium Powders Are Used for 3D Printing?
The main powders are:
– Ti6Al4V (Grade 5 or 23) – common for medical, dental, and industrial use.
– Beta 21S –high-strength applications like aerospace and motorsport.
– Grade 4 (pure titanium) – corrosion-resistant, for chemical, marine, and biomedical parts.
– TA15 – optimized for aerospace and specialized high-performance applications.
In Which Industries Is Titanium Used in 3D Printing?
Titanium 3D printing is mainly used in:
– medicine (e.g., implants and prosthetics),
– dental technology (customized restorations),
– aerospace (lightweight, corrosion-resistant components),
– motorsport (exhaust systems, suspension components),
– and toolmaking (mold inserts with cooling channels).
How is the Material Change handled in Titanium 3D Printing?
Switching materials requires complete removal of powder residues to avoid contamination. Thorough cleaning and safety measures ensure material quality and process reliability.
Further links:

Author: Markus Wolf
Passionate about 3D printing, while being
CTO and Co-Founder of 2onelab.